
Electronic Signature: A Comprehensive Guide
As the world embraces the digital age, organizations have never been more focused on establishing a secure foundation for their transformation efforts. Whether it be safeguarding consumer transactions or enabling safe citizen journeys, government agencies and businesses alike need a way to seamlessly authenticate identities across an increasingly distributed landscape.
Fortunately, that’s where solutions like secure and identity-verified electronic signatures come in. With a well-protected electronic signing infrastructure, organizations can future-proof interactions and protect themselves from the risks of our rapidly evolving environment.
Read on to learn more about electronic signatures, including what they are, how they work, and how you can take advantage.
What is an electronic signature?
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is an efficient way to sign a digital document. As a replacement to the traditional signing process, it allows the signer to attach their name to any record or transaction by electronic means — no paper involved.
Think of an e-signature as a virtual representation of a person. Much like its paper signature counterpart, it’s used to:
- Certify the authenticity of a legal document
- Establish intent to be bound by the terms of a signed document
The electronic signing process can have the same legal effect as a handwritten signature, so long as it adheres to certain requirements, which may vary by location. With various security measures in place, you can sign any legal document with total confidence.
Why are electronic signatures necessary?
The handwritten signature process is relatively simple. You open a paper document, sign your name above the signature line, and your work is complete. Now, in our digital world, it’s not quite so easy.
Electronic transactions are increasingly common, especially with the rise of remote work, e-commerce, and online business models. Consequently, consumers, governments, and organizations alike need a way to certify documents and prove intent regardless of their location.
More importantly, they must do so with the utmost security. As electronic transactions skyrocket, so too do the associated risks — forgery, repudiation, and other legal disputes.
A handwritten signature normally has the protection of witnesses who can testify to its authenticity. However, e-signatures must rely on more sophisticated mechanisms. Fortunately, as technology advances, electronic signature software and other solutions are enabling entities to certify exactness and authenticity with ease.
What’s the difference between an electronic and digital signature?
Simply put, an electronic signature is an umbrella term that describes the overall technology used to certify, authenticate, and sign a digital document. By contrast, a digital signature is a type of e-signature that provides a higher level of trust.
Digital signatures are widely recognized as best practice for verifying electronic transactions because they rely on public key infrastructure (PKI). In simple terms, PKI is a credential system that issues cryptographic assets called digital certificates, which can only be obtained from a certificate authority (CA) such as Entrust. A digital certificate works like a passport; each one is unique to the signer, therefore acting as proof of identity.
The signature process leverages a special cryptographic asset known as a document signing certificate. When someone electronically signs a legal document, the certificate embeds a copy of itself into the signature, alongside a timestamp of when it was signed.
What’s more, digital signatures are calculated based on the exact contents of the document. That means subsequent changes will break the signature, helping you avoid tampering and repudiation.
In combination, these functionalities prevent the signer from denying the existence or validity of a digital document or their signature. Moreover, they provide the confidence to communicate, transact, and do business remotely without compromising security or trust.
3 major types of electronic signatures
In most parts of the world, electronic signatures are typically categorized by their level of assurance, which is to say how well they guarantee the intent, consent, and identity of the signer. This is meant to provide a standardized way of assessing and understanding their reliability.
Generally, there are three tiers of e-signature assurance:
- Low assurance: Any signature in electronic form might be considered an e-signature. In fact, it can be as simple as a mouse-drawn signature, a scanned paper signature pasted onto a digital document, or even a name typed into a PDF. Unfortunately, these basic forms can be easily disputed.
- High assurance: Digital signatures are much more reliable by nature. Because they use public key infrastructure and digital certificates, they’re much harder to counterfeit or dispute. Plus, digital signatures are tamper-evident and prevent the contents of a signed document from being altered.
- Regulated high assurance: Digital signatures that are regulated by legislation are considered the most trustworthy. In addition to PKI and document signing certificates, these signatures must be compliant with local standards. Moreover, signing infrastructure is normally maintained by entities called “trust service providers” (TSPs) that are subject to auditing and strict regulation.
Signature example: eIDAS regulation
Specific rules, standards, and definitions vary from country to country. However, most jurisdictions that legally accept electronic signatures maintain the multi-tiered approach outlined above — albeit with their own specifications.
There’s perhaps no better example of this than the European Union (EU). In 2016, the EU enacted eIDAS, which stands for “electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services.” This regulation established the legal framework for e-signatures across all EU member states, harmonizing all jurisdictions under a single legislation.
There are three types of signatures under eIDAS:
- Simple electronic signature: As the most basic electronic signature available, this type doesn't require strong signer authentication or identity verification, making it the easiest to implement. However, it also offers the least assurance.
- Advanced electronic signature: This type has more precise requirements and may ask the signer to verify their identity with biometrics, access codes, digital certificates, and other electronic means.
- Qualified electronic signature: More sophisticated than an advanced electronic signature with stronger technical requirements, this type offers the highest level of assurance. Both advanced and qualified signatures are in fact digital signatures, but the latter is the more secure and tightly regulated of the two.
Notably, a qualified electronic signature has to meet stringent requirements. Not only must they include an eIDAS-qualified digital certificate, but they also should be generated using a qualified token or Signature Creation Device (SCD), issued by a qualified TSP.
What is a Signature Creation Device?
An SCD is a hardware device designed to host digital certificates and generate digital signatures. Two of the most common types include USB tokens and hardware security modules (HSMs).
In the case of a USB token, users insert the device directly into their computer, which allows them to access their digital certificate. On the other hand, HSMs are stored either on a local corporate network or in a TSP-hosted cloud where people can access and generate signatures without any impact on the user experience.
A Qualified Signature Creation Device (QSCD) is one that’s been vetted through the eIDAS certification process. Only QSCDs can use qualified digital certificates to generate a qualified signature.
What are electronic signatures used for?
According to Deloitte, the global e-signing market will be worth over $14 billion by 2026, growing at an impressive 30% annual rate. Much of this can be attributed to supportive regulation around the world, not to mention an expansive list of industry use cases.
Here’s how different sectors are leveraging electronic signatures to their advantage:
Financial services
Financial institutions like banks and credit unions have traditionally relied on paper-based processes for a variety of business applications. Now, with the help of electronic and digital signatures, they can maximize trust and reduce risk — both for themselves and consumers.
Take customer onboarding, for example. In the past, banks required new customers to open accounts by physically visiting a branch and writing their wet signature on a piece of paper. Now, with secure digital signatures, institutions can streamline account opening by allowing customers to electronically sign forms, disclosures, and other agreements.
Plus, because digital signatures are time-stamped and tamper-evident, they act as an electronic audit trail that can’t be easily disputed in case of disagreement.
Sales contracts
No matter the industry, a sales contract is often a business’ most important legal document. Whether it be a Scope of Work (SOW) or a Managed Service Agreement (MSA), contracts carry a significant weight and must be created, written, and signed with total confidence. However, the traditional signing process can be slow and needlessly complicated.
With e-signatures, organizations can expedite the document signing process without sacrificing security. Identity verification is fast and seamless, empowering both parties to sign the dotted line regardless of their time or location. This can help accelerate the sales cycle and reduce the need for physical paperwork.
Government services
In the government arena, there are many types of agreements that require an accurate and accessible audit trail. From compliance documents and policy changes to equipment requisitions and benefit applications, electronic signatures can help agencies and citizens simplify and secure the entire workflow.
For instance, imagine applying for financial assistance from your local government. Rather than taking time off work and traveling to the office itself, citizens can use an electronic signature solution to submit an electronic form. Not only does this speed up the process, but it also increases accountability and visibility with a digital record of submission.
Human resources
As reported by Forbes, human resource (HR) departments often use e-signatures for documents related to hiring and recruitment. Onboarding a new employee requires a lot of paperwork, but with an e-signature solution, the signer can complete contracts without ever leaving their home. This is especially important for remote employees who may not live in proximity to the office.
Which signature is right for you?
Indeed, electronic signatures are making waves in countless ways. That said, each application is different — some may require a higher level of confidence in the signer’s identity, intent, and consent to sign. For example, signing a mortgage is a much more sensitive transaction than signing for a delivery.
In turn, not all e-signatures are created equal, making it possible to adjust proof levels to minimize risk for particular circumstances. Because of the legal value carried by a signature, it's crucial to work with the appropriate legal advisor to ensure that the proofs gathered during the signing process are aligned and compliant with the regulations that apply, and sufficient in case of dispute.
It’s best practice to keep the following in mind when choosing a signature type:
- Country and state legislation, such as the U.S. e-Sign Act
- Cross-border regulation, such as eIDAS in the European Union
- Industry requirements, like Know Your Customer (KYC) or Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws
Benefits of an electronic signature solution
Why should your organization adopt electronic signatures? In truth, there are plenty of reasons. A secure electronic signature solution can help you realize a host of significant benefits, including:
- Flexibility: Sign an electronic document from anywhere at any time. With e-signatures, you can improve employee and customer experience with quicker, more efficient, more user-friendly processes.
- Security: Authenticate every transaction and fight fraud across all digital agreements. Better yet, limit the threat of reputational damage by increasing legal assurance and reducing liability exposure.
- Innovation: Accelerate your signing process with measurable improvements in speed and efficiency. E-signatures optimize the deployment of integrated agreement workflows, allowing you to maximize productivity while strengthening resilience.
- Compliance: Produce a digital audit trail and ensure alignment with local, national, and international regulations, including in the United States, European Union, and beyond.
How does electronic document signing work?
Although the technology behind electronic document signing may sound nuanced and sophisticated, the user experience is actually quite seamless. In fact, it may only take minutes from start to finish.
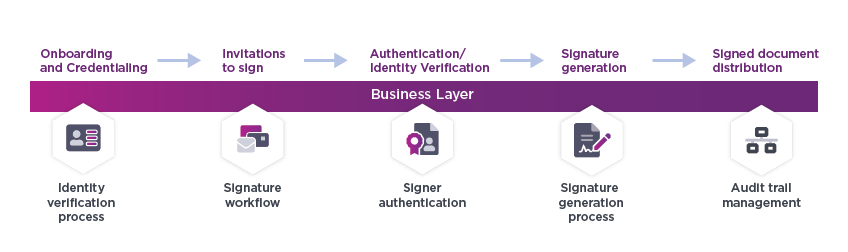
Generally, this happens in five basic steps:
- Onboarding and credentialing: First, the user or organization is set up within the document signing system. It verifies the identity of the user and/or their organization, often through multiple authentication methods.
- Signature request: Once onboarding is complete, the system initiates a signature request by selecting the digital document they want to be signed and inviting the necessary parties.
- Identity verification: Before a signer can add their electronic signature, they must authenticate themselves to ensure integrity and security. This is usually done using multi-factor authentication (MFA), such as email or SMS confirmation. If the signers have not gone through the onboarding step initially, an identity verification process can be triggered at this stage.
- Signature generation: The signature generation process depends on the type of signature chosen. In the case of a simple electronic signature, a scribble may be added to the document. If digital signatures are generated, document signing certificates will be generated by the TSP for each signer verified. The certificates will be used to generate the signatures. A unique transaction ID will be created, and every step of the process is recorded into an audit trail for legal purposes.
- Signed document distribution: After all signatures are collected, the signed document is securely stored for future reference. Users can access a secure copy for their own records.
Secure transactions with Entrust
Trust is essential to digital transformation. The good news? Entrust makes transformation as frictionless as possible with a complete portfolio of electronic signature solutions for organizations of all shapes and sizes.
Whether you’re an enterprise, government agency, or anything in between, our globally trusted certificate services, nShield HSMs, and robust identity platform enable strong, secure signing no matter your needs. The products and services that support our identified signing portfolio can be individually integrated or bundled into a full-stack solution. These include:
- Entrust Remote Signing Service, a cloud-based solution for issuing and hosting digital certificates and generating secure digital signatures
- Entrust Signing Automation Service, a cloud-based solution that empowers organizations to issue branded certificates and digital seals
- Entrust Document Signing Certificates, which allow you to create trusted individual or employee signatures using secure USB tokens or HSMs
- Entrust Identity as a Service, a managed offering that provides trusted identity management for workforces, consumers, and citizens through robust, phishing-resistant MFA
- Signhost by Evidos — an Entrust company — provides a cloud solution for orchestrating signature requests, authenticating signers, generating signatures, and distributing documents in one comprehensive platform.
Backed by industry-leading technology aligned with global standards, Entrust is here to help you harness the power of electronic signing. As experts in PKI, HSMs, authentication, and digital signatures, you can trust us to provide a best-in-class, high-assurance solution that matches your unique needs.
